Delving into the realm of thermochemistry, the Heats of Reaction and Hess’s Law Lab provides a hands-on investigation into the energy changes that accompany chemical reactions. By exploring the fundamental concepts of heats of reaction and the powerful tool of Hess’s law, this lab empowers students to unravel the mysteries of energy transfer in chemical systems.
Through meticulously designed experiments, students will gain a profound understanding of the exothermic and endothermic nature of reactions, the role of bond breaking and formation in energy exchange, and the remarkable ability of Hess’s law to predict reaction enthalpies. The lab culminates in a comprehensive analysis of experimental data, leading to a deeper appreciation of the quantitative aspects of thermochemistry.
Heats of Reaction and Hess’s Law: Heats Of Reaction And Hess’s Law Lab

Introduction, Heats of reaction and hess’s law lab
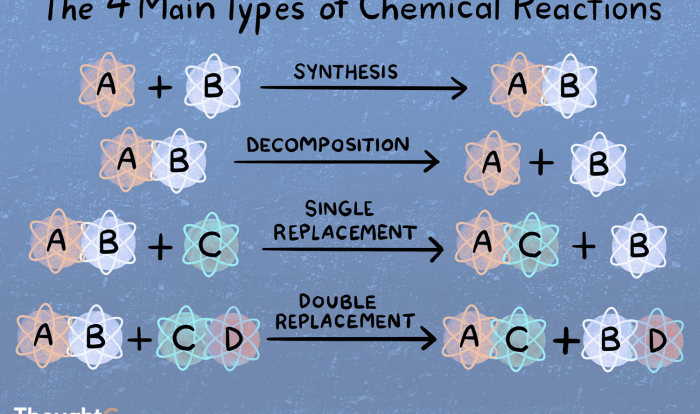
Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that accompany chemical reactions. Heats of reaction are the amounts of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction. Hess’s law is a powerful tool that allows us to calculate the heats of reaction for complex reactions using the heats of reaction for simpler reactions.
Experimental Setup
The materials and equipment needed for this lab include a calorimeter, a thermometer, a balance, and a variety of chemicals. The experimental procedure involves measuring the change in temperature of the calorimeter when a chemical reaction is carried out inside it.
The heat of reaction is then calculated using the following equation:
“`q = mcΔT“`where q is the heat of reaction, m is the mass of the calorimeter and its contents, c is the specific heat of the calorimeter and its contents, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Data Analysis
The experimental data can be analyzed by plotting a graph of the temperature of the calorimeter versus time. The heat of reaction is then calculated from the slope of the graph.
“`q =
mCcal(ΔT/Δt)
“`where q is the heat of reaction, m is the mass of the calorimeter and its contents, C calis the specific heat of the calorimeter and its contents, ΔT is the change in temperature, and Δt is the change in time.
Calculations
Hess’s law can be used to calculate the heats of reaction for complex reactions using the heats of reaction for simpler reactions. The following equation is used to calculate the heat of reaction for a reaction:
“`ΔH rxn= ΣΔH f(products)
ΣΔHf(reactants)
“`where ΔH rxnis the heat of reaction, ΔH f(products) is the sum of the heats of formation of the products, and ΔH f(reactants) is the sum of the heats of formation of the reactants.
Applications
Heats of reaction and Hess’s law have a wide variety of applications in chemistry. They can be used to:
- Predict the spontaneity of a reaction
- Calculate the equilibrium constant for a reaction
- Design new chemical processes
FAQs
What is the significance of heats of reaction in chemistry?
Heats of reaction provide crucial information about the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions, helping us understand the stability and reactivity of compounds.
How does Hess’s law simplify thermochemical calculations?
Hess’s law allows us to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using a series of intermediate steps, even if the overall reaction cannot be measured directly.
What are the applications of heats of reaction and Hess’s law in real-world scenarios?
These concepts find applications in various fields, including industrial process optimization, combustion engineering, and the development of new energy sources.