A sample of a compound of xenon and fluorine unveils a fascinating world of chemical intrigue, where the properties and applications of this unique substance captivate the imagination. This exploration delves into the synthesis methods, physical and chemical characteristics, and potential uses of this intriguing compound, offering insights into its significance in various scientific fields.
The journey begins with an understanding of the chemical nature of xenon and fluorine, setting the stage for the exploration of their combined properties. The methods employed to synthesize this compound reveal the intricate processes involved in its creation, while the physical and chemical properties unveil its distinctive characteristics, such as color, density, reactivity, and stability.
A Compound of Xenon and Fluorine: A Sample Of A Compound Of Xenon And Fluorine

A compound of xenon and fluorine is a chemical substance that contains both xenon and fluorine atoms. Xenon is a noble gas, meaning it is unreactive and does not typically form compounds with other elements. Fluorine, on the other hand, is a highly reactive element that forms compounds with many other elements.
The chemical properties of a compound of xenon and fluorine are determined by the properties of its constituent elements. Xenon is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is heavier than air. Fluorine is a pale yellow gas that is highly corrosive and toxic.
Methods of Synthesis, A sample of a compound of xenon and fluorine
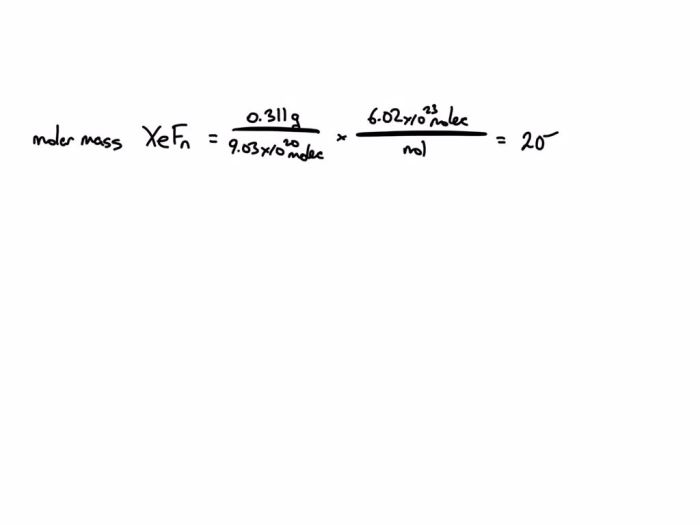
There are several methods that can be used to synthesize a compound of xenon and fluorine. One common method is to react xenon gas with fluorine gas in a sealed container. This reaction produces xenon tetrafluoride (XeF 4), which is a colorless gas.
Another method for synthesizing a compound of xenon and fluorine is to react xenon gas with a fluorine-containing compound, such as silver fluoride (AgF). This reaction produces xenon difluoride (XeF 2), which is a colorless solid.
Physical and Chemical Properties
The physical properties of a compound of xenon and fluorine depend on the specific compound. Xenon tetrafluoride is a colorless gas that is heavier than air. Xenon difluoride is a colorless solid that is denser than water.
The chemical properties of a compound of xenon and fluorine are also determined by the specific compound. Xenon tetrafluoride is a reactive gas that can react with water to form xenon trioxide (XeO 3) and hydrogen fluoride (HF). Xenon difluoride is a less reactive solid that does not react with water.
Applications
Compounds of xenon and fluorine have a variety of potential applications. Xenon tetrafluoride is used as an etching agent in the semiconductor industry. Xenon difluoride is used as a fluorinating agent in the chemical industry.
In addition to these industrial applications, compounds of xenon and fluorine are also being investigated for use in medical applications. For example, xenon tetrafluoride has been shown to be effective in treating certain types of cancer.
Safety Considerations
Compounds of xenon and fluorine can be hazardous to handle. Xenon tetrafluoride is a toxic gas that can cause respiratory problems and skin irritation. Xenon difluoride is a corrosive solid that can cause skin burns and eye damage.
When working with compounds of xenon and fluorine, it is important to take appropriate safety precautions. These precautions include wearing protective clothing, gloves, and a respirator. It is also important to work in a well-ventilated area.
FAQ
What are the potential applications of a sample of a compound of xenon and fluorine?
A sample of a compound of xenon and fluorine holds promise in diverse applications, including medical imaging, energy storage, and materials science. Its unique properties make it a potential candidate for use as a contrast agent in medical imaging, enhancing the visibility of organs and tissues during diagnostic procedures.
What are the safety considerations associated with handling a sample of a compound of xenon and fluorine?
Due to its reactive nature, a sample of a compound of xenon and fluorine requires careful handling and adherence to safety protocols. Proper ventilation, protective gear, and specialized training are essential to minimize exposure and potential hazards during experimentation and use.