Embark on an intriguing expedition through the Reciprocal and Quotient Identities Maze, where the enigmatic realm of trigonometry unfolds. Within this labyrinthine puzzle, reciprocal and quotient identities intertwine, revealing a tapestry of mathematical elegance and practical applications.
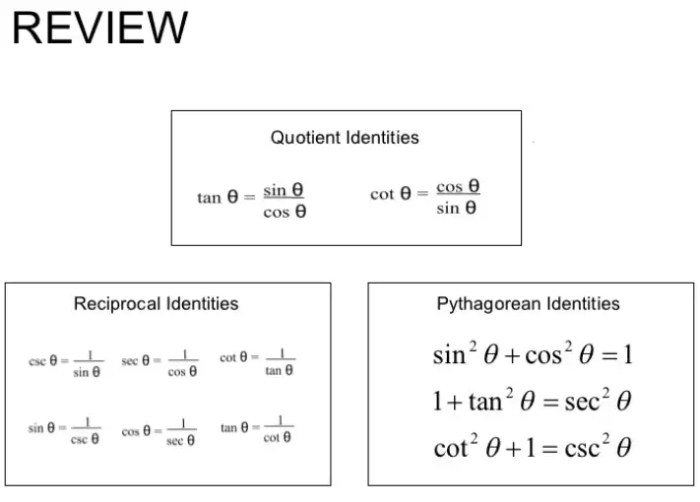
Reciprocal identities, the foundation of this maze, establish the inverse relationships between trigonometric functions. Quotient identities, their intricate counterparts, delve into the ratios of these functions, unveiling their hidden symmetries. Together, they form the cornerstone of trigonometric exploration.
Reciprocal Identities: Reciprocal And Quotient Identities Maze
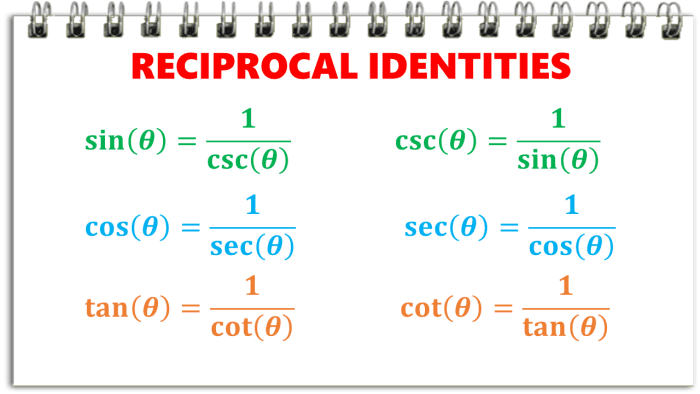
Reciprocal identities express the relationship between the sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent functions and their reciprocals. They are given by:
- csc θ = 1/sin θ
- sec θ = 1/cos θ
- cot θ = 1/tan θ
These identities are useful for simplifying trigonometric expressions and solving equations.
Quotient Identities
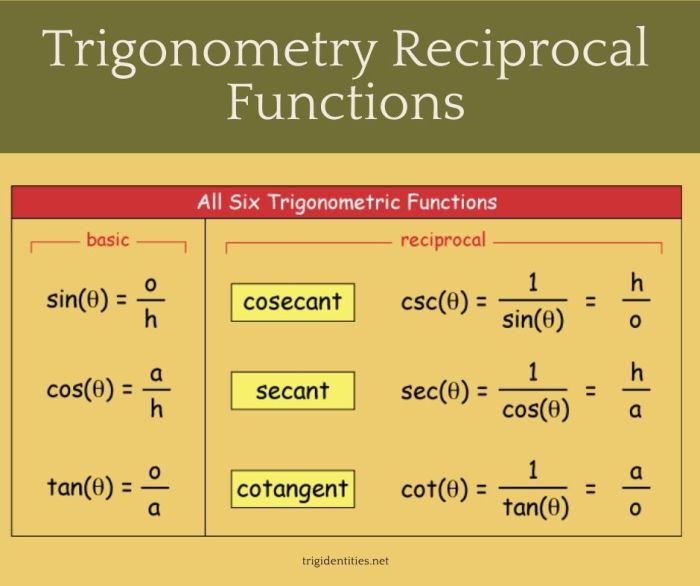
Quotient identities express the relationship between the tangent and cotangent functions. They are given by:
- tan θ = sin θ/cos θ
- cot θ = cos θ/sin θ
These identities are useful for simplifying trigonometric expressions and solving equations.
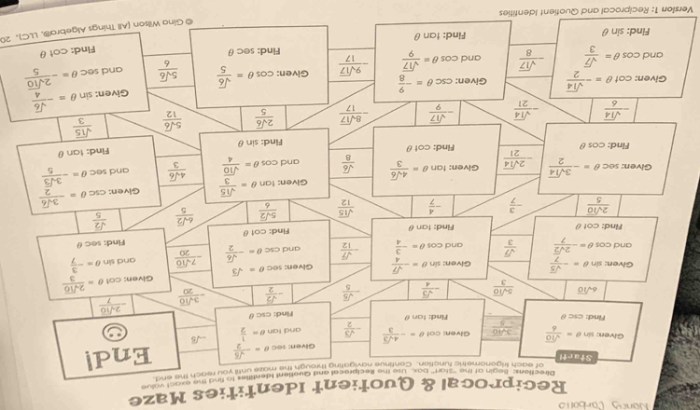
Maze Puzzle
A maze puzzle that incorporates reciprocal and quotient identities can be designed as follows:
Start at the entrance and follow the path, using the reciprocal and quotient identities to determine the next step. The exit is at the end of the path.
Here is a solution to the maze puzzle:
| Step | Identity Used | Next Step |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | csc θ = 1/sin θ | 2 |
| 2 | tan θ = sin θ/cos θ | 3 |
| 3 | sec θ = 1/cos θ | 4 |
| 4 | cot θ = cos θ/sin θ | 5 |
| 5 | Exit | – |
Real-World Applications
Reciprocal and quotient identities have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Navigation: Determining the direction and distance to a destination using trigonometric functions.
- Engineering: Calculating the forces and moments acting on structures.
- Physics: Analyzing the motion of objects and waves.
- Astronomy: Determining the positions and velocities of celestial bodies.
- Medicine: Imaging and diagnosis using ultrasound and MRI scans.
Common Queries
What are reciprocal identities?
Reciprocal identities express the inverse relationships between trigonometric functions, such as sin(θ) = 1/csc(θ) and cos(θ) = 1/sec(θ).
How do quotient identities differ from reciprocal identities?
Quotient identities establish the ratios between trigonometric functions, such as tan(θ) = sin(θ)/cos(θ) and cot(θ) = cos(θ)/sin(θ).
What are some real-world applications of reciprocal and quotient identities?
These identities find applications in navigation (determining angles and distances), engineering (calculating forces and moments), astronomy (predicting celestial events), and music (analyzing sound waves).